The Resurgence of M&A In The Tech Middle Market
The Power of Technology and Middle-Market M&A: Driving Global Innovation
Imagine an ecosystem where trillions of dollars flow annually, fueling innovation, creating millions of jobs, and reshaping industries. This is the world of technology—a ubiquitous force propelling the global economy. As of 2023, the global tech industry contributed over $5.2 trillion annually, accounting for approximately 5-6% of global GDP. Employing more than 70 million people worldwide, hubs such as Silicon Valley, Shenzhen, and Bangalore drive groundbreaking advancements that, along with the resurgence of M&A, continue to redefine industries and societies.
In the United States, the tech sector contributes $2 trillion annually, representing nearly 10% of the national economy and employing over 12 million individuals. Europe, with an €800 billion annual contribution, leads emerging sectors like fintech, health tech, and green technology. Venture capital funding reached an astounding $330 billion globally in 2022, underscoring the tech industry’s critical role in driving innovation and growth.
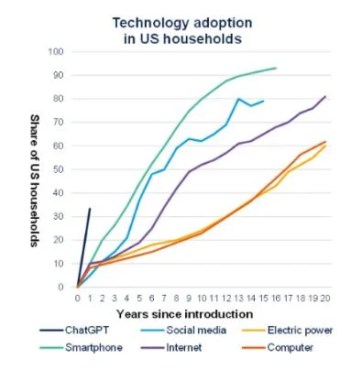
Source: Our World in Data
Middle-Market M&A: A Resurgence of Strategic Deals
The resurgence of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) within the tech sector highlights the industry’s resilience and adaptability. After peaking at $1.24 trillion in global tech M&A deals in 2021, the market slowed due to economic uncertainties. However, stabilizing interest rates and increased liquidity have fueled a robust comeback—marking a clear resurgence of M&A activity, particularly in middle-market transactions valued between $10 million and $500 million. These deals, largely driven by private equity and venture-backed firms, are reshaping the competitive landscape.
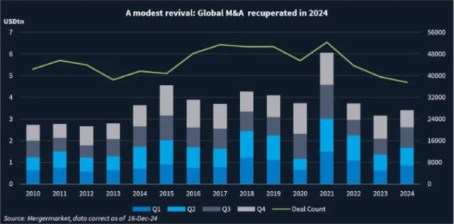
Source: Mergermarket
Understanding the Middle Market in Tech M&A
Middle-market transactions encompass deal sizes ranging from $10 million to $500 million, segmented into:
- Lower Middle Market: $10M–$50M
- Core Middle Market: $50M–$250M
- Upper Middle Market: $250M–$500M
These transactions often involve high-growth, privately held companies that have progressed beyond initial funding stages. Middle-market M&A serves as a vital link between early-stage funding and large-scale consolidation, driving innovation and expansion within the tech sector.
The Importance of Middle-Market M&A
1. Nurturing Innovation
- Acquiring Niche Startups: Middle-market acquisitions often target specialized startups in cutting-edge domains like artificial intelligence (AI), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These deals expedite the adoption of disruptive technologies, granting acquirers access to advanced intellectual property (IP) and expertise.
- Risk-Tolerant Growth: Middle-market firms maintain agility, enabling them to embrace calculated risks and experiment with groundbreaking ideas.
- Access to Talent: Acqui-hiring secures specialized talent in high-demand areas like AI development, software engineering, and cybersecurity.
2. Bridging Funding and Consolidation
- Transition from VC/PE: Middle-market companies often mature beyond Series C funding, becoming prime targets for acquisition as they scale operations.
- Pipeline for Mega-Deals: These firms serve as feeder targets for larger-scale M&A, integrating into the ecosystems of tech giants to drive innovation and market penetration.
3. Economic and Strategic Value
- Economic Growth: Middle-market M&A fosters job creation, competitive dynamics, and advancements in key industries such as fintech, cybersecurity, and AI.
- Strategic Expansion: Acquirers leverage these transactions to expand into new markets, broaden product offerings, and strengthen competitive positioning.
Trends in Middle-Market Tech M&A
1. Key Industries Driving Activity
- SaaS: Scalable subscription models remain in high demand across sectors like healthcare and logistics.
- AI: Investments in generative AI and machine learning platforms continue to surge.
- Cybersecurity: Middle-market firms lead next-generation solutions like zero-trust architectures.
- Fintech: Startups in payment solutions, insurtech, and blockchain transform financial ecosystems.
- Greentech/Climate Tech: ESG initiatives drive investments in renewable energy and carbon management technologies.
2. Geographic Focus
- North America: Dominates global deal activity, with hotspots like Silicon Valley excelling in AI, SaaS, and cybersecurity.
- Europe: Cities like London and Berlin lead in fintech and greentech, despite regulatory hurdles.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth in edtech and SaaS, with emerging hubs in India and Southeast Asia.
- Latin America: Fintech and e-commerce thrive, driven by markets in Brazil and Mexico.
3. Shifts in Buyer Profiles
- Private Equity: PE firms dominate middle-market M&A, drawn by predictable cash flows and scalable models like SaaS.
- Corporate Buyers: Tech giants pursue smaller acquisitions to bypass regulatory scrutiny and achieve strategic synergies.
Implications of Middle-Market Trends
- Competitive Advantage for Buyers: Middle-market M&A offers innovation and market expansion opportunities with reduced regulatory challenges compared to mega-deals.
- Regional Ecosystem Growth: Cross-border deals foster globalized tech ecosystems, while localized acquisitions strengthen regional hubs.
- Regulatory and Strategic Shifts: These transactions benefit from lighter regulatory scrutiny, enabling faster integration and reduced compliance costs.
Why the Resurgence of Middle-Market Tech M&A?
Recent data underscores the resurgence of middle-market tech M&A. In Q4 2024 alone, middle-market deal volumes grew by 20% year-over-year, indicating a robust recovery trajectory. While overall global deal volumes in the technology sector declined by 36% during the first half of 2024 compared to 2023, deal values surged by 54%, reflecting a strong emphasis on high-value middle-market transactions.
Private equity firms have also played a critical role, increasingly targeting mid-sized tech companies due to their predictable cash flows and growth potential. Technology deals accounted for 83% of middle-market volumes and 74% of values during this period, with AI, SaaS, and cloud technologies emerging as dominant themes. Several factors drive the renewed focus on middle-market transactions:
Economic Adjustments Fueling Growth
Economic conditions have shifted significantly, with lower interest rates and stabilizing financial markets creating a conducive environment for deal-making. As of January 2025, the all-in cost of capital is approximately 150 basis points lower than it was a year ago. This reduction has enhanced access to financing, making it easier for firms to pursue acquisitions. Such shifts reflect a broader trend of economic adjustments favoring agile, middle-market transactions over larger, capital-intensive deals.
Valuations Create Opportunities
The market corrections of 2022 resulted in a downward adjustment of valuations for many startups, particularly in the technology sector. This correction has unlocked opportunities for strategic buyers to acquire innovative companies at more reasonable prices. With startups now offering advanced capabilities at reduced valuations, middle-market M&A is becoming an efficient pathway for firms looking to enhance their portfolios without overspending.
Innovation Push Driving Strategic Deals
The rapid advancement of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has placed immense pressure on companies to innovate continuously. Middle-market acquisitions provide a streamlined route for larger corporations to integrate cutting-edge capabilities without the lengthy development cycles associated with organic innovation. Recent trends highlight the demand for digital transformation, with 75% of Fortune 500 companies planning portfolio adjustments within the next year to incorporate innovative solutions.
Strategic Positioning for Competitive Advantage
In an era of technological disruption, middle-market acquisitions offer a strategic means for companies to bolster their market positions, diversify offerings, and enhance operational efficiencies. Unlike mega-deals, which often face logistical and integration challenges, middle-market transactions allow firms to achieve these objectives with greater agility. Notably, sectors such as AI and cloud technology are at the forefront of this activity, as firms aim to stay ahead in the race for technological supremacy.
Regulatory Advantages of Middle-Market Transactions
Regulatory concerns continue to play a pivotal role in shaping M&A strategies. While mega-deals frequently face antitrust scrutiny, middle-market transactions often proceed with fewer regulatory hurdles. This reduced oversight accelerates deal closures, reduces compliance costs, and minimizes risk, making smaller acquisitions a more attractive option for companies seeking rapid expansion or diversification.
Case Study: Shopify’s Acquisition of Deliverr
Source: Deliverr
In May 2022, Shopify’s $2.1 billion acquisition of Deliverr marked a transformative move in e-commerce logistics. Structured as approximately 80% cash and 20% Shopify Class A Subordinate Voting Shares, the acquisition aimed to empower small and medium-sized businesses with advanced fulfillment capabilities.
Strategic Rationale
- Enhanced Fulfillment: Deliverr’s predictive analytics and inventory management tools optimize supply chains, enabling faster delivery options.
- Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions: The integration of Deliverr’s technology provides greater flexibility to navigate logistical challenges.
- Democratizing Logistics: Shopify’s mission to level the playing field for smaller merchants is reinforced by this acquisition.
Operational Impact
- Logistics Expansion: Deliverr enhances inventory distribution strategies, ensuring quicker delivery times.
- Job Creation: The acquisition has spurred workforce growth, contributing to sectoral economic development.
Pre- and Post-Acquisition Insights
Deliverr’s Pre-Acquisition Performance
Before its acquisition, Deliverr was a formidable player in the fulfillment sector, processing over one million orders monthly and serving prominent clients like eBay and Walmart. This operational expertise provided a solid foundation for Shopify to build upon.
Post-Acquisition Expectations
The integration has positioned Shopify to redefine fulfillment in e-commerce. By combining Deliverr’s network with its existing infrastructure, Shopify can offer merchants a seamless end-to-end fulfillment solution. This aligns with broader market trends: the global fulfillment market, valued at $86 billion in 2021, is projected to nearly double to $198.62 billion by 2030, signaling immense growth potential for Shopify’s expanded logistics capabilities.
Role of Private Equity and Venture Capital in Middle-Market M&A
Private equity and venture capital firms are pivotal in middle-market M&A, targeting scalable, high-potential assets:
- Increased Activity: PE accounted for nearly 40% of tech M&A activity in 2023, with over $1.2 trillion in dry powder globally.
- Partnership Trends: Collaborations between PE/VC firms and strategic buyers enhance financial and operational synergies, reshaping the M&A landscape.
- Shift Toward Growth Equity: The focus on growth equity—funding expansion rather than early-stage ventures—has further driven middle-market activity. Key areas of interest include AI, cybersecurity, green tech, and data analytics, sectors that promise high returns and align with long-term growth strategies.
The Big 5’s Cautious M&A Strategy: Why Tech Giants Are Holding Back
Once at the forefront of merger and acquisition activity, the Big 5—Microsoft, Google, Apple, Amazon, and Meta—are now taking a more cautious approach. Their M&A activity has notably slowed, as the focus has shifted from external acquisitions to internal growth, particularly in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI). Collectively, these tech giants are investing a staggering $200 billion annually in data centers and GPUs to build proprietary technologies that strengthen their competitive edge.
Key Factors Behind the M&A Slowdown
Several key factors are shaping the Big 5’s shift away from acquisitions:
- AI-Centric Investments
The race to develop proprietary AI models and infrastructure is a central focus for these companies. With billions of dollars being poured into AI development, cash reserves that might otherwise be used for acquisitions are being redirected to enhance their internal capabilities. This strategic investment in AI has become a top priority, as these companies seek to dominate the next frontier of tech. - Regulatory Hurdles
Antitrust scrutiny has become a major barrier to M&A activity. Increased investigations by regulatory bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and Department of Justice (DOJ) have created a challenging environment for large tech companies pursuing acquisitions. Microsoft’s attempt to acquire Activision Blizzard faced significant delays and regulatory pushback, highlighting the complexities these companies face when pursuing large-scale mergers. - Organic Growth Strategies
Rather than relying on acquisitions, the Big 5 are prioritizing organic growth through in-house innovation. By investing in product development and technology enhancements, companies like Apple and Amazon are reducing their reliance on external acquisitions as a means to stay competitive, focusing instead on cultivating homegrown solutions. - High Cash Reserves, Low M&A Activity
Despite holding record-high cash reserves, the Big 5 are demonstrating caution in their M&A strategies. Their combined $370 billion cash balance is being largely earmarked for capital expenditures, particularly in the area of AI infrastructure, which is projected to reach $250 billion in 2025. Although their significant market value increases make stock-based acquisitions attractive, these companies are not leveraging their financial strength to pursue such opportunities.
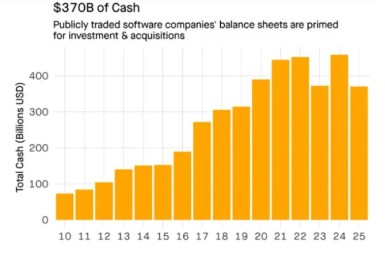
Source: Theory Ventures
External Challenges Amplifying the M&A Slowdown
The external business environment has also played a role in curbing M&A activity:
- Antitrust Scrutiny: Regulatory bodies have intensified their focus on market competition, making large-scale mergers more difficult to execute. This has resulted in delays and uncertainty surrounding major acquisitions, like Microsoft’s bid for Activision Blizzard.
- Investor Focus on Profitability: Investors are shifting their priorities towards profitability, urging companies to focus on delivering sustainable earnings rather than growth through acquisitions. This shift has led to a more cautious approach to M&A, with many business executives indicating they are less likely to pursue acquisitions in the near term.
- Economic Uncertainties: Ongoing economic volatility, including inflation and fluctuating interest rates, has further contributed to cautious cash management. Companies are holding on to cash reserves and are more reluctant to make risky investments in acquisitions during uncertain times.
- AI and Buybacks: In lieu of pursuing acquisitions, many tech giants are redirecting resources to enhance their AI capabilities and engage in stock buybacks. Companies like Alphabet and Meta are focusing on innovation and shareholder value rather than expanding through M&A.
Strategic Shifts: Partnerships Over Acquisitions
In response to the complexities of M&A, many tech companies are exploring strategic partnerships as an alternative means of growth. Collaborations in areas such as AI and cloud computing allow companies to innovate and build synergies without the regulatory hurdles associated with full acquisitions. This shift towards partnerships signals a more measured approach to expansion, one that prioritizes agility and internal development over the complexity of mergers.
Future Outlook: A Resilient Path for Middle-Market Tech M&A
As we move further into 2025, the middle-market tech M&A landscape is showing signs of resilience and adaptation in response to economic challenges. While early 2023 saw a notable slowdown in deal activity, with only 11 middle-market tech deals reported compared to 48 in January 2022, the outlook remains cautiously optimistic. Companies are recalibrating their strategies to navigate these uncertainties, positioning themselves for a resurgence of M&A activity and a robust recovery.
The future of middle-market tech M&A looks promising, driven by several key trends:
- Increased Interest from Private Equity
Private equity firms, sitting on substantial reserves of dry powder, are poised to remain active in the middle market. With over $1.2 trillion in uninvested capital, they are positioned to capitalize on favorable financing conditions as interest rates are expected to decrease. This influx of capital will likely fuel continued deal activity, especially in sectors primed for consolidation. - Focus on Fragmented Industries
As companies look for growth opportunities, fragmented industries remain a primary target for consolidation. Buyers will continue to seek out acquisitions in these sectors, where merging smaller players can yield enhanced efficiencies and greater market share. This trend presents a pathway for strategic acquisitions that can unlock value through integration. - Adaptation to Economic Challenges
Tech companies are expected to embrace innovative and creative solutions to overcome current economic hurdles. With lower borrowing costs anticipated, companies will be better equipped to navigate the market and execute deals that support long-term growth. The flexibility to adapt to shifting conditions will be a key factor in the success of these companies moving forward.
As of January 16, 2025, the projected reduction in interest rates is also poised to have a significant impact on middle-market tech M&A activity, potentially accelerating the resurgence of M&A across the sector. Here’s how the anticipated shifts in financing conditions are expected to influence the landscape:
- Lower Financing Costs: Reduced interest rates will make acquisition financing more attractive, leading to a boost in M&A activity. With cheaper capital, buyers will be more inclined to pursue deals, enabling aggressive bidding for high-quality targets.
- Potential Increase in Valuation Multiples: As the cost of capital decreases, purchase price multiples (such as EV/EBITDA) may rise. Historically, low interest rates have been linked to higher valuations, as companies are willing to pay a premium when financing costs are more favorable. This could narrow the valuation gap that has previously held back transactions.
- Boosted Investor Confidence: As financing conditions improve, stock market valuations may increase, leading to heightened investor confidence. This positive sentiment is likely to drive more strategic acquisitions as companies feel more secure in their financial positions.
- Strategic Focus on Growth: Lower financing costs may shift the focus of investments toward more disciplined, long-term growth strategies, particularly in high-potential sectors like AI and green tech. Companies may also pursue strategic partnerships with private equity firms or venture capitalists, leveraging their financial resources to execute targeted acquisitions.
In conclusion, while economic uncertainties have shaped the M&A landscape in recent years, the future outlook for middle-market tech M&A is increasingly positive. As financing conditions improve, investor confidence rises, and companies focus on strategic, disciplined growth, we can expect to see a resurgence of M&A and a surge in deal activity throughout 2025 and beyond.









